Manage users
Overview
This documentation provides API methods for managing users in WordPress via REST API. Below, you will find details on retrieving user data, filtering users, sorting responses, and handling authentication.
All API requests below require Basic Authentication.
Get Last Login Date for a User
Definition:
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/users/{id}
Example Request
https://{url}/wp-json/wp/v2/users/{id}
Note
Pay attention to the meta fields in the response.
{
"meta": {
"persisted_preferences": {
"core/edit-post": {
"isComplementaryAreaVisible": true,
"welcomeGuide": false,
"openPanels": ["post-status", "page-attributes", "featured-image"]
},
"_modified": "2024-03-09T08:18:09.934Z"
},
"icds_binding": 3,
"icds_timezone": "+00:00",
"icds_locale": "en_US",
"icds_disabled": 0,
"icds_last_login": "2024-03-20T08:30:14+00:00",
"icds_meta": {
"icds_binding": 3,
"icds_locale": "en_US",
"icds_timezone": "+00:00",
"icds_disabled": 0,
"icds_last_login": "2023-03-20T08:30:14+00:00"
},
"icds_binding_ref": {
"Name": "Chaunce Perrie",
"Id": "4fc12b21-686a-ed11-81ac-00224892b4a1",
"LogicalName": "contact",
"KeyAttributes": null
}
}
}
The icds_last_login field shows the last login date. It can be empty if the user hasn’t signed in.
How to Filter Users
GET method
- The following method allows filtering users using complex query conditions.
Definition:
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/users/context=edit&icds_filter={conditions}
Example
https://{{baseUrl}}/wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&icds_filter=[{"Field": "icds_binding","Operator": "eq","Value": "1"}]
When a header is used, the JSON text does not have to be encoded, but cannot contain newlines. Or encode this body using URL-encoded format (you can use any tool).
Other examples:
[
{
"Field": "icds_binding",
"Operator": "eq",
"Value": "1"
},
{
"Field": "icds_binding_ref",
"Operator": "ne",
"Value": null
}
]
Example with encoded json
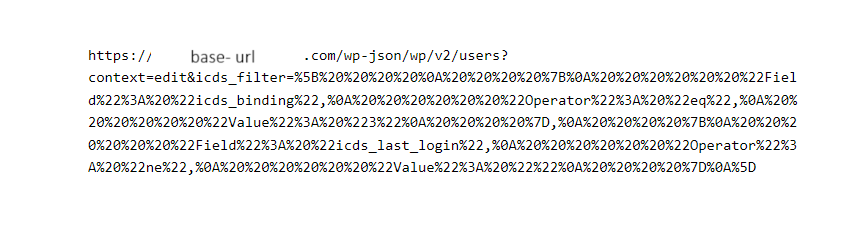
Parameter: icds_filter={encodedPart}.
You can add as many elements as you want. Operators can be: eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le, =, !=, >, <, >=, <=, LIKE, IN, BETWEEN, REGEXP, EXISTS.
Examples
| Operator | icds_filter value |
|---|---|
| like | [{"Field": "user_name", "Operator": "LIKE", "Value": "*adam*"}] |
| like | [{"Field": "user_name", "Operator": "LIKE", "Value": "on"}] |
| like | [{"Field": "email", "Operator": "LIKE", "Value": "*@huffingtonpost.com"}] |
| like | [{"Field":"user_id","Operator":"like","Value":"1113c9dc-ff0d-ef11-9f89-0022489310b4"}] |
| like | [{"Field": "icds_binding_ref", "Operator": "like", "Value": "Mateo Passman"}] |
| eq | [{"Field": "email", "Operator": "eq", "Value": "vsearight7@huffingtonpost.com"}] |
| ne | [{"Field": "icds_locale", "Operator": "ne", "Value": "en_US"}] |
| GT | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": "GT", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
| GE | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": "GE", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
>= | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": ">=", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
> | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": ">", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
| LT | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": "LT", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
| LE | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": "LE", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
<= | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": ">=", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
< | [{"Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": ">", "Value": "2025-03-20"}] |
GET method with multiple conditions
- Another way to filter users:
Definition:
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&query={conditions}
https://{baseUrl}/wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&query={"Filter": {"Type": "and", "Conditions": [{"Field": "user_name", "Operator": "eq", "Value": "adil"}]}, "Order": [{"Field": "id", "Dir": "asc"}], "Select": ["id", "email", "first_name"]}
Parameters:
context=edit– Retrieves detailed user information.query={encodedJSON}– Encoded JSON defining filtering conditions.
Filtering Logic:
- Filter conditions support multiple fields using AND or OR logic.
- Operators include comparison (
>,<,=,like,in,exists, etc.). - Ordering sorts results based on specified fields.
- Selection limits the response to relevant fields.
JSON Schema for Query:
{
"$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"$id": "https://alexacrm.com/data/rest-api-users.schema.json",
"title": "REST API Users request extended",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"Filter": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"Type": { "enum": ["and", "or"] },
"Conditions": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"Field": { "type": "string" },
"Operator": { "enum": ["eq", "ne", "gt", "ge", "lt", "le", "like", "in", "between", "regexp", "exists"] },
"Value": { "type": ["string", "number", "null"] }
},
"required": ["Field", "Operator", "Value"]
}
}
},
"required": ["Type", "Conditions"]
},
"Order": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"Field": { "type": "string" },
"Dir": { "enum": ["asc", "desc"] }
},
"required": ["Field", "Dir"]
}
},
"Select": {
"type": "array",
"items": { "type": "string" },
"minItems": 1,
"uniqueItems": true
}
}
}
GET method using the X-Icds-Filter header
- One more way to filter users is to use the X-Icds-Filter header.
Definition:
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/users/context=edit&icds_filter_header=1
Example
https://{your-wordpress-site}/wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&icds_filter_header=1
Parameter: icds_filter_header=1.
Header: The value of the header can be:
[
{
"Field": "icds_binding",
"Operator": "eq",
"Value": "1"
},
{
"Field": "icds_binding_ref",
"Operator": "ne",
"Value": null
}
]
Note: When using the X-Icds-Filter header, the JSON filter conditions must NOT be URL-encoded.
POST Method: Filtering Users with Payload
Definition
POST /wp-json/integration-cds/v1/users
Example Request:
https://{baseUrl}/wp-json/integration-cds/v1/users
Request Body:
{
"Filter": {
"Type": "and",
"Conditions": [
{ "Field": "icds_last_login", "Operator": ">", "Value": "2025-01-01" },
{ "Field": "email", "Operator": "like", "Value": "%huffingtonpost.com" }
]
},
"Order": [
{ "Field": "email", "Dir": "desc" },
{ "Field": "icds_last_login", "Dir": "asc" }
],
"Select": [
"id", "email", "username", "name", "first_name", "last_name", "roles",
"meta"
]
}
How to Get Only Necessary User Fields in Response
Definition
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&icds_select_header=1
Example
https://{your-wordpress-site}/wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&icds_select_header=1
Parameter: icds_select_header=1 .
Header: use the X-Icds-Select header. Here you can specify any fields you want to see for users, for example, id, email, description, url.
In this example, you will see only the id, email, description, and url fields for the WordPress users.
How to Sort Users by Fields in Response
Definition
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&icds_order_header=1
Example
https://{your-wordpress-site}/wp-json/wp/v2/users?context=edit&icds_order_header=1
Parameter: icds_order_header=1.
Header: Add the X-Icds-Order header. Here you can specify the field name to sort users, for example, url or username.
How to Send a Password Reset Message
To send a password reset message to a user, you can use one of the following:
Definition
POST /wp-json/integration-cds/v1/reset_password?email={userEmail}&id={userId}&login={userLogin}
Example
https://{your-wordpress-site}/wp-json/integration-cds/v1/reset_password?email={userEmail}&id={userId}&login={userLogin}
To identify the user, the request should contain one of the following parameters:
- id: WordPress user ID
- email: User email
- login: User login for the WordPress site
The parameters priority is: id, email, login.
This request will send a password reset link to the user and return an empty body (204 response). In case of an error, it will return a 500 response with the error description:
{
"code": 3,
"message": "User not found.",
"data": null
}
Generate a password reset link.
Definition
GET /wp-json/integration-cds/v1/reset_password_link?email={userEmail}
Example
https://{your-wordpress-site}/wp-json/integration-cds/v1/reset_password_link?email=user@example.com
To identify the user, the request should contain one of the following parameters:
- id: WordPress user ID
- email: User email
- login: User login for the WordPress site
It will return a JSON response with a password reset link or an error description in case of an error:
{
"link": "https://your-wordpress-site.com/wp-login.php?action=rp&key=HEA7wLLCEvtnV3Ick1bQ&login={username}&wp_lang=en_US"
}